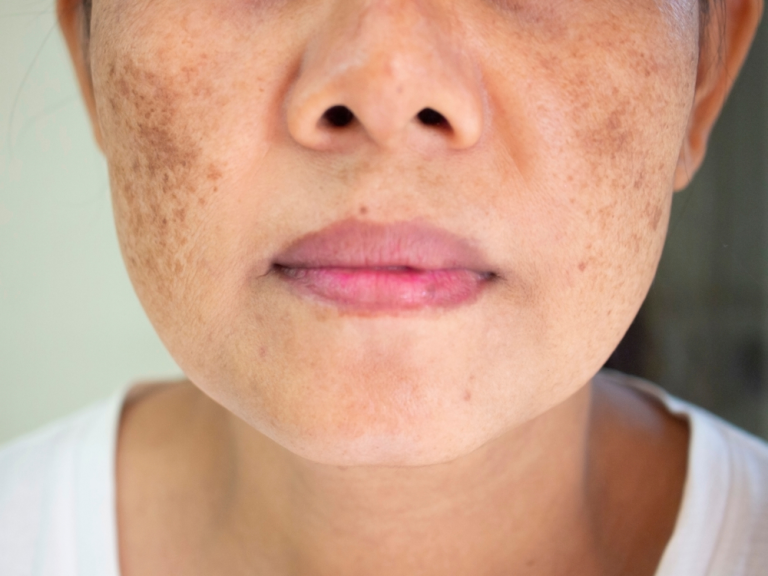
In your journey towards beautiful, radiant skin, remember that melasma treatment is not just a destination; it’s a transformational path to reclaiming your confidence and embracing your natural beauty. Melasma may have tested your self-esteem, but it doesn’t define you. As you explore the causes, symptoms, and solutions for melasma, you’re taking the empowering step towards regaining control over your skin’s story.
What is Melasma?
Melasma is a common skin condition characterised by the development of brown or greyish-brown patches on the skin, primarily on the face. It is often called “the mask of pregnancy” because it frequently occurs in pregnant women. However, melasma can affect anyone, regardless of gender or age.
The condition is primarily driven by the overproduction of melanin, the pigment responsible for the colour of our skin, hair, and eyes. Melasma patches typically appear on areas of the skin that are exposed to sunlight, such as the cheeks, forehead, upper lip, and chin. While melasma is not a harmful medical condition, it can be aesthetically distressing and impact an individual’s self-esteem.
Who is at Risk for Melasma?
Melasma is a skin condition that can affect individuals of various backgrounds, but certain factors can increase the risk of developing it. Those at a higher risk for melasma typically include:
1. Gender – Women are more commonly affected by melasma than men, with estimates suggesting that about 90% of melasma cases occur in women. Hormonal fluctuations, such as those associated with pregnancy and birth control pills, can contribute to its development.
1. Gender – Women are more commonly affected by melasma than men, with estimates suggesting that about 90% of melasma cases occur in women. Hormonal fluctuations, such as those associated with pregnancy and birth control pills, can contribute to its development.
2. Prevention of Worsening – Melasma can worsen if left untreated, especially if the underlying triggers, such as sun exposure or hormonal changes, are not addressed. Treating melasma early can help prevent it from becoming more pronounced and harder to manage.
3. Psychological Well-Being – Skin conditions like melasma can lead to psychological distress, including anxiety and depression. Treating melasma can alleviate some of these emotional burdens and promote mental health.
4. Protection Against Sun Damage – Melasma patches are particularly sensitive to UV radiation. By seeking treatment, individuals are often educated about the importance of sun protection and can adopt habits that reduce the risk of further pigmentation.
5. Prevention of Recurrence – Effective treatment addresses existing melasma and helps prevent its recurrence. Dermatologists can recommend maintenance strategies, such as skincare routines and lifestyle modifications, to minimise the chances of melasma returning.
6. Health and Medical Evaluation – In some cases, melasma may indicate an underlying medical condition or hormonal imbalance. Seeking treatment can lead to a proper evaluation by a healthcare specialist to rule out any other health concerns.
7. Customized Solutions – Treatment for melasma is not one-size-fits-all. Dermatologists can provide personalised treatment plans tailored to an individual’s skin type, lifestyle, and underlying causes. This ensures the most effective and safe approach to managing the condition.
8. Advancements in Treatment – There have been significant advancements in melasma treatment options. Newer therapies and technologies offer improved outcomes, making it more feasible than ever to manage melasma effectively.
Melasma treatment is essential for cosmetic reasons and the overall well-being of individuals affected by this skin condition. Seeking professional guidance and treatment can improve skin health, increase self-confidence, and improve quality of life.
What Causes Melasma?
Melasma is a complex skin condition whose exact cause is not fully understood. However, several factors are believed to contribute to the development of melasma. These factors include:
1. Sun Exposure – Ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun is a primary trigger for melasma. Sun exposure stimulates the production of melanin (skin pigment), and individuals with melasma are often more sensitive to UV radiation. Melasma patches typically appear on skin areas exposed to the sun, such as the face.
2. Hormonal Changes – Hormonal fluctuations play a significant role in melasma development. This is why melasma is often called “the mask of pregnancy.” Hormonal changes associated with pregnancy, birth control pills, hormone replacement therapy, and menopause can increase the risk of melasma. The hormones estrogen and progesterone are thought to influence melanin production.
3. Genetics – There appears to be a genetic predisposition to melasma. If you have a family history of the condition, you may be more likely to develop it yourself.
4. Cosmetic Products and Procedures – Certain skincare products and cosmetic procedures, particularly those that irritate the skin, can trigger or worsen melasma. This is known as post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
5. Ethnicity and Skin Type – Melasma is more common in individuals with darker skin tones, such as those of Asian, Hispanic, African, or Middle Eastern descent. People with Fitzpatrick skin types III to VI, which include a higher level of melanin, are more susceptible.
6. Thyroid Disorders – In some cases, thyroid disorders, such as hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism, have been associated with melasma.
Melasma is often a multifactorial condition, which may result from a combination of these factors. Genetic predisposition, hormonal changes, and sun exposure are the primary culprits for many individuals.
While the exact cause of melasma may not be fully understood, managing the condition typically involves addressing these contributing factors.
How is Melasma Diagnosed?
Melasma is typically diagnosed through a visual examination by a healthcare specialist, most commonly a dermatologist or skincare specialist. The diagnosis is primarily based on the appearance of the skin, the distribution of pigmented patches, and a discussion of the patient’s medical history and potential triggers. Here’s how the diagnosis process for melasma typically works:
1. Medical History – Your healthcare specialist will begin by asking about your medical history, including any previous skin conditions, medications, hormonal changes (such as pregnancy or menopause), and your family history of skin disorders.
2. Skin Examination – The healthcare specialist will visually inspect the affected areas of your skin, looking for characteristic signs of melasma. These signs include brown or greyish-brown patches, their distribution on the face (typically the cheeks, forehead, upper lip, and chin), and any other relevant skin changes.
3. Wood’s Lamp Examination – This handheld ultraviolet (UV) light can help highlight the extent and depth of pigmentation in the skin. It can aid in determining the severity of melasma and assessing the response to treatment.
4. Skin Biopsy (Rarely) – While not commonly needed, in some instances, a skin biopsy may be performed to rule out other skin conditions that can mimic melasma, such as certain fungal infections or skin cancers. A small sample of skin is taken and examined under a microscope.
5. Discussion of Triggers – Your healthcare specialist may discuss potential triggers or exacerbating factors for melasma, such as sun exposure, hormonal changes, or specific skincare products.
6. Differential Diagnosis – In some cases, other skin conditions that cause pigmentation changes, such as post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation or drug-induced pigmentation, may need to be ruled out. This helps ensure an accurate diagnosis.
Once a diagnosis of melasma is confirmed, your healthcare specialist can work with you to develop an appropriate treatment plan tailored to your specific needs. Melasma is a chronic condition that may require ongoing management to minimise pigmentation and prevent recurrence. Sun protection and adherence to a prescribed skincare regimen are often essential to melasma management.
What Can You Do to Prevent Melasma?
Preventing melasma can be challenging, but there are several strategies you can implement to reduce your risk of developing this skin condition or minimise its severity if you are already prone to it. Here are some tips for preventing melasma:
1. Sun Protection – Sun exposure is a primary trigger for melasma. To protect your skin from UV radiation, follow these guidelines:
Wear Sunscreen– Use broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher daily, even on cloudy days. Apply it to all exposed skin, including your face, neck, and hands. Reapply every two hours, especially if you’re outdoors.
Seek Shade– Stay in the shade during peak sunlight, typically between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m.
Wear Protective Clothing– Cover your face and skin with wide-brimmed hats, sunglasses, and long-sleeved clothing when spending time outdoors.
Wear Sunscreen– Use broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher daily, even on cloudy days. Apply it to all exposed skin, including your face, neck, and hands. Reapply every two hours, especially if you’re outdoors.
Seek Shade– Stay in the shade during peak sunlight, typically between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m.
Wear Protective Clothing– Cover your face and skin with wide-brimmed hats, sunglasses, and long-sleeved clothing when spending time outdoors.
2. Hormonal Management – If you are prone to melasma due to hormonal changes, consider discussing hormone-related treatments or contraceptive options with your healthcare specialist who may have a lower risk of triggering melasma.
3. Avoid Irritating Products – Be cautious when using skincare products and cosmetics. Avoid harsh or irritating ingredients, as these can exacerbate melasma. Consult with a dermatologist to select skincare products suitable for your skin type.
4. Limit Heat Exposure– Prolonged exposure to heat, such as hot baths or saunas, can potentially worsen melasma. Try to limit such exposures, especially if you have melasma-prone skin.
5. Cosmetic Procedures – Some cosmetic procedures, like laser treatments or chemical peels, can worsen melasma if not performed by experienced professionals. If you’re considering such treatments, consult a dermatologist specialising in melasma to discuss the risks and benefits.
6. Manage Stress – Chronic stress can trigger hormonal changes that may exacerbate melasma. Implement stress-management techniques like mindfulness, meditation, or yoga to help keep stress levels in check.
7. Consult a Dermatologist – If you have a family history of melasma or are at increased risk due to your skin type, consider consulting a dermatologist for a personalised prevention plan. They can guide the most effective preventive measures and recommend suitable products for your skin.
8. Pregnancy Planning – If you’re planning to become pregnant and have a history of melasma, consult your healthcare specialist to discuss strategies to minimise the risk of melasma during pregnancy.
While these strategies can help reduce the risk of melasma and its severity, some individuals may still develop the condition despite their best efforts.
Can Sun Protection Alone Improve Melasma?
Sun protection is crucial to managing and improving melasma, but there may be other solutions for some. While proper sun protection can help prevent melasma from worsening and reduce the risk of new pigmentation, it may not eliminate existing melasma patches. The effectiveness of sun protection in improving melasma can vary depending on factors such as the severity of the condition and an individual’s commitment to sun-safe practices.
Here’s how sun protection can benefit individuals with melasma:
1. Preventing Worsening – Ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun is a known trigger for melasma. By diligently protecting your skin from the sun, you can prevent further darkening of existing melasma patches and reduce the risk of new ones forming.
2. Minimizing Pigmentation – Sun protection can help lighten melasma patches over time by preventing further melanin production. Over several months, this can lead to a gradual improvement in the appearance of melasma.
3. Preventing Recurrence – Even if you have undergone treatment for melasma and achieved significant improvement, sun protection is essential to prevent the condition from recurring. Melasma returns if the skin is exposed to UV radiation without adequate protection.
To effectively use sun protection as part of your melasma management plan, consider the following tips:
Use Sunscreen – Apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher to all sun-exposed areas of your skin daily. Reapply outdoors every two hours, and use a water-resistant sunscreen if swimming or sweating.
Seek Shade – Stay in the shade during peak sunlight hours, typically between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m., to minimise direct sun exposure.
Wear Protective Clothing– Cover your face and body with protective clothing, such as wide-brimmed hats, sunglasses, and long-sleeved shirts and pants.
Avoid Tanning – Avoid tanning beds and sunbathing, as these activities increase your risk of melasma and skin damage.
Limit Outdoor Activities – Reduce your time outdoors during peak sunlight hours.
Seek Shade – Stay in the shade during peak sunlight hours, typically between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m., to minimise direct sun exposure.
Wear Protective Clothing– Cover your face and body with protective clothing, such as wide-brimmed hats, sunglasses, and long-sleeved shirts and pants.
Avoid Tanning – Avoid tanning beds and sunbathing, as these activities increase your risk of melasma and skin damage.
Limit Outdoor Activities – Reduce your time outdoors during peak sunlight hours.
While sun protection is essential, seeing noticeable improvements in existing melasma patches may take time. For some individuals, additional treatments, such as topical creams, chemical peels, or laser therapy, may be recommended by a dermatologist to complement sun protection efforts and achieve more significant results.
What Are the Common Prescription Medications for Melasma?
Prescription medications for melasma are typically recommended when over-the-counter treatments and lifestyle modifications alone do not provide satisfactory results. These prescription medications are often prescribed by dermatologists and are used to target melasma at a deeper level. Some common prescription medications for melasma include:
1. Topical Hydroquinone – Hydroquinone is one of the most frequently prescribed medications for melasma. It works by inhibiting the production of melanin in the skin. Prescription-strength hydroquinone is available in concentrations of up to 4%. Dermatologists may recommend hydroquinone-based creams or lotions for melasma treatment.
2. Topical Tretinoin (Retin-A) – Tretinoin is a prescription topical retinoid that helps improve melasma by increasing skin cell turnover and promoting the shedding of melanin-containing skin cells. It can be used in combination with hydroquinone for enhanced efficacy. Tretinoin should be used cautiously, as it can cause skin irritation and increased sensitivity to the sun.
3. Topical Corticosteroids – In some cases, dermatologists may prescribe topical corticosteroids to reduce inflammation and lighten melasma patches. Corticosteroids should be used under close medical supervision due to potential side effects and should not be used for extended periods.
4. Triple Combination Creams – Some prescription treatments combine multiple active ingredients to target melasma from various angles. For example, a triple combination cream might contain hydroquinone, tretinoin, and a topical corticosteroid. These combination therapies can be effective but should be used under the guidance of a dermatologist.
5. Topical Azelaic Acid – Azelaic acid is a prescription medication that can help lighten melasma patches by inhibiting melanin production. It is available in gel or cream formulations and is often used as an alternative to hydroquinone for individuals who cannot tolerate or prefer to avoid hydroquinone.
6. Tranexamic Acid – Tranexamic acid is an oral medication that a dermatologist can prescribe to treat melasma. It works by inhibiting the production of pigment and reducing inflammation. This medication is typically reserved for severe cases of melasma.
Prescription medications for melasma should only be used under the supervision and guidance of a healthcare specialist. They may also be part of a comprehensive treatment plan that includes sun protection measures and ongoing maintenance to prevent melasma recurrence.
The choice of medication and treatment plan will depend on the individual’s condition and needs. Consulting with a dermatologist is essential to determine the most appropriate prescription medication and treatment approach for melasma.
What Cosmetic Procedures Can Help Treat Melasma?
Several cosmetic procedures can effectively treat melasma by targeting pigmentation and promoting skin rejuvenation. Dermatologists or trained skincare professionals typically perform these procedures. It’s essential to consult with a healthcare specialist to determine the most suitable cosmetic procedure for your specific type of melasma and skin type. Here are some standard cosmetic procedures that can help treat melasma:
1. Chemical Peels– Chemical peels involve the application of a chemical solution to the skin, which exfoliates the top layers and promotes skin regeneration. Chemical peels can be superficial, medium-depth, or deep, depending on the depth of the pigmentation and the desired results. Superficial peels, such as glycolic acid or salicylic acid peels, are often used for melasma and can help lighten pigmentation.
2. Laser Therapy– Laser treatments can target melanin in the skin and help improve melasma. Different lasers, such as fractional or intense pulsed light (IPL) devices, may break down pigmentation and stimulate collagen production. Experienced dermatologists or laser specialists should perform these treatments.
3. Microneedling – Microneedling involves using tiny needles to create controlled micro-injuries in the skin. This process stimulates collagen production and can help improve the appearance of melasma over time. Microneedling can be combined with topical treatments for enhanced results.
4. Fractional Radiofrequency – Fractional radiofrequency treatments use radiofrequency energy to heat the skin and stimulate collagen production. These procedures can help reduce the appearance of melasma and improve overall skin texture.
5. IPL (Intense Pulsed Light) Therapy– IPL therapy uses light energy to target and break down melanin in the skin. It can effectively reduce the appearance of pigmented lesions, including melasma. Multiple IPL sessions may be required for optimal results.
6. Topical Agents in Conjunction with Procedures – In many cases, cosmetic procedures are combined with topical agents (e.g., hydroquinone or tretinoin) to enhance the outcomes of melasma treatment. Your healthcare specialist may recommend this combination approach.
7. Cryotherapy – Cryotherapy involves using extreme cold to destroy unwanted pigmented cells. It is typically used for localised areas of melasma or isolated pigmented lesions.
8. Microdermabrasion – Microdermabrasion exfoliates the skin using a mechanical device or fine crystals, which can help improve the texture and pigmentation of the skin. While it may benefit melasma, it is generally considered less effective than other procedures.
Melasma can be challenging to treat, and results may vary from person to person. Multiple treatment sessions may be necessary to achieve the desired outcome. Additionally, strict sun protection measures are essential before and after cosmetic procedures to prevent melasma from worsening or recurring.
What to Expect After Melasma Treatment?
What you can expect after melasma treatment can vary depending on the specific treatment method used and the individual’s response. However, there are some everyday experiences and general guidelines that can help you understand what to expect after melasma treatment:
1. Temporary Redness and Irritation – Many melasma treatments, such as chemical peels, laser therapy, and microneedling, can cause temporary redness, swelling, and irritation in the treated area. This is a normal part of the skin’s healing process and typically resolves within a few days to a week, depending on the treatment intensity.
2. Sun Sensitivity – After melasma treatment, your skin may be more sensitive to sunlight, so it’s crucial to continue practising strict sun protection. Wear sunscreen with a high SPF and protective clothing, and avoid direct sun exposure, especially during healing.
3. Post-Treatment Care – Your healthcare specialist will provide you with specific post-treatment care instructions. This may include avoiding certain skincare products, such as retinoids or alpha hydroxy acids, until your skin fully recovers.
4. Peeling and Flaking – Some treatments, like chemical peels, may lead to skin peeling or flaking as the top layers shed. This normal exfoliation process can reveal fresher, brighter skin underneath.
5. Gradual Improvement– The results of melasma treatment are often delayed. It may take several weeks to months to see significant improvement in the appearance of melasma. Be patient and continue following your treatment plan.
6. Maintenance and Follow-Up – Depending on the severity of your melasma and the treatment method used, you may require ongoing maintenance treatments to prevent melasma from recurring. Your healthcare specialist will discuss the recommended follow-up schedule with you.
7. Skincare Routine – After melasma treatment, it’s essential to maintain a consistent skincare routine. Your healthcare specialist may recommend specific products to help maintain your results and prevent the reappearance of melasma.
8. Avoid Sunburn – It’s crucial to avoid sunburn at all costs, as it can exacerbate melasma and cause new pigmentation. Continue to be vigilant about sun protection, especially during the healing phase.
9. Skin Hydration– Keeping your skin well-hydrated is essential for its overall health and can help heal. Consider using a gentle, hydrating moisturiser as recommended by your healthcare specialist.
10. Follow-Up Consultations – Depending on your treatment plan, you may have follow-up consultations with your healthcare specialist to assess the progress of your melasma treatment and make any necessary adjustments.
The key to successful melasma treatment is consistency and adherence to your healthcare specialist’s recommendations. Contact your specialist for guidance and support if you have any concerns or experience unexpected side effects after melasma treatment.
By addressing melasma, you’re not just improving your skin’s appearance; you’re enhancing your quality of life, protecting your skin’s health, and nurturing your mental well-being. Your unique path to treatment is a testament to your individuality, and the advancements in melasma treatment offer hope and promise.
Embrace the journey, celebrate your progress, and trust your ability to shine. Your skin’s natural brilliance is waiting to emerge, and with each step forward, you’re one step closer to the beautiful, empowered, and confident you you’ve always been.